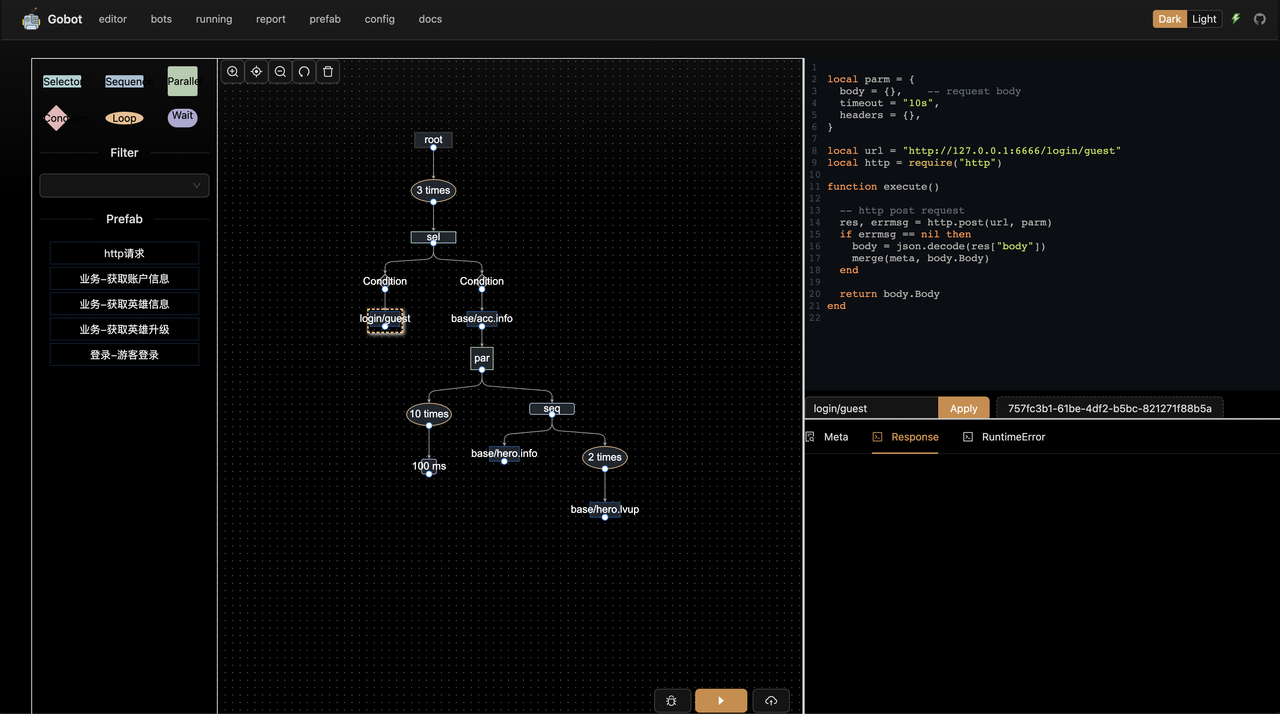
Gobot is a powerful stateful API testing robot. It provides a graphical interface for building test scenarios, allows for easy test script writing, step-by-step debugging and pressure testing, and can share and store states between each stage of the testing process.
- windows
- Go to the release page and download the executable program.
- Run the server by executing the run.bat file in the gobot_driver_win_x64_v0.3.8 directory.
- Run the editor program by executing gobot.ext in the gobot_editor_win_x64_v0.3.8 directory.
- Fill in the address input window that pops up or the address bar on the config page with http://127.0.0.1:8888, the local server address.
- Utilizes the 'behavior tree' to control the robot's execution order and uses 'scripts' for specific node behaviors, such as making HTTP requests.
- Provides graphical editing and debugging capabilities.
- Allows creating and reusing 'prefab' template nodes in the configuration page.
- Supports driving via HTTP API (post /bot.run -d '{"Name":"a robot"}'), making it easy to integrate into CI.
- Supports multiple protocol formats (HTTP, TCP, WebSocket...) and supports pack/unpack of byte streams at the script layer
- Offers 'stress testing' with configurable concurrency settings on the configuration page.
Through built-in modules and scripts, we can have rich logical expression capabilities. We can also use global (single bot) meta structures to maintain various state changes of the bot.
--[[
Each node has its own independent .lua script for execution. When a node is executed, the script is loaded and run using dostring.
Users can load desired 'modules' into the script for additional functionalities. For more information, refer to the documentation.
The script allows defining node execution logic, like sending an HTTP request.
]]--
-- Users can load "modules" they want to use in the script.
-- document https://pojol.github.io/gobot/#/
local http = require("http")
-- request body
req = {
body = {}, -- post body
timeout = "10s", -- http timeout
headers = {}, -- http headers
}
-- When the robot runs to a node, the execute function will be executed.
function execute()
-- Here, users can define the execution logic of nodes themselves (for example, sending an HTTP request)
res, err = http.post("url", req)
-- todo
-- state - State code
-- res - Information displayed in the Response panel
return state.Succ, res
end| Module | interface | Description |
|---|---|---|
| base64 | encode decode |
Provides base64 encoding/decoding functionality. |
| http | post get put |
Support HTTP connection. |
| tcp | dail close write read |
Support TCP connection. |
| websocket | dail close write read |
Support WebSocket connection. |
| protobuf | marshal unmarshal |
Provides Protobuf operations. |
| mongoDB | insert find update delete ... |
Provides MongoDB operations. |
| json | encode decode |
Offers JSON functionalities. |
| md5 | sum |
Calculates MD5 hashes. |
| utils | uuid random |
Generates random values, UUIDs. |
| ... | More modules available. |
Example message.lua is located in script/. Users can refer to its implementation and modify the protocol packet parsing method in their own projects
-- message.lua
--[[
| 2 byte | 1 byte | 2 byte | 2byte | |
|msg len | proto type | custom | msgid | |
| header | body |
]]--
function TCPUnpackMsg(msglen, buf, errmsg)
if errmsg ~= "nil" then
return 0, ""
end
local msg = message.new(buf, ByteOrder, 0)
local msgTy = msg:readi1()
local msgCustom = msg:readi2()
local msgId = msg:readi2()
local msgbody = msg:readBytes(2+1+2+2, -1)
return msgId, msgbody
end
function TCPPackMsg(msgid, msgbody)
local msglen = #msgbody+2+1+2+2
local msg = message.new("", ByteOrder, msglen)
msg:writei2(msglen)
msg:writei1(1)
msg:writei2(0)
msg:writei2(msgid)
msg:writeBytes(msgbody)
return msg:pack()
end
-- use
--------------------------------------------------------
-- Serialize using proto.marshal
-- Assemble TCP packet using TCPPackMsg
local reqbody, errmsg = proto.marshal("HelloReq", json.encode({
Message = "hello",
}))
ret = conn.write(TCPPackMsg(1002, reqbody))
--------------------------------------------------------
-- 2 is the designed byte length of the message length, conn will first attempt to read the specified bytes for parsing the message size
-- Parse protocol message content based on msgid
-- TCPUnpackMsg can be user-defined, not necessarily returning in the form of msgid, msgbody, it can also be msghead, msgbody depending on the user's message structure design
msgid, msgbody = TCPUnpackMsg(conn.read(2))
if msgid == 1002 then
body = proto.unmarshal("HelloRes", msgbody)
endTry the editor out on website driver server address http://47.120.59.203:8888